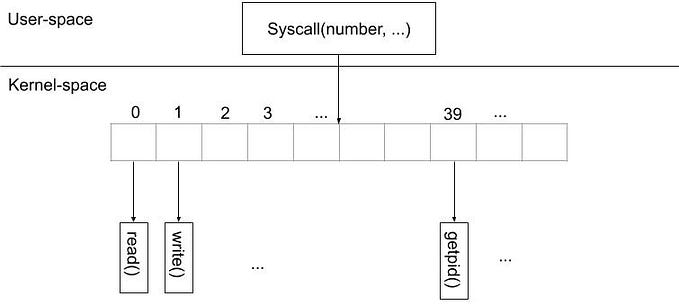
SYSTEM PROGRAMMING
Build the Linux Kernel
Based on Ubuntu
This quick tutorial shows you how to update to the latest kernel. It is to be used in a virtual machine as there is a risk of system failure. It is only for education purpose. Please use it at your own risk.

1. Install Required Packages
sudo apt-get install git fakeroot build-essential ncurses-dev xz-utils libssl-dev bc flex libelf-dev bison2. Get the Kernel Source Code
We can clone the Github repository directly using this command:
git clone https://github.com/torvalds/linux.git3. Configure the Kernel
To configure the kernel we are going to use the current kernel’s configuration and update it. To do this, simply execute these commands:
cd linux/
cp /boot/config-$(uname -r) .config
yes "" | make oldconfigThe last command will set any new configuration of the new kernel to its default value.
4. Building the Kernel
makeYou may hit an error indicating that there is “No rule to make target ‘debian/canonical-certs.pem”. To fix the error use these commands:
scripts/config --disable SYSTEM_REVOCATION_KEYS
scripts/config --disable SYSTEM_TRUSTED_KEYSYou can also manually edit the .config file and remove the keys, setting an empty value instead.
5. Install the New Kernel
Warning: Once you execute the following commands it will update to the new kernel. Please use it at your own risk.
sudo make modules_install
sudo make installThese two commands will install the new kernel and its modules and configure the system to reboot into it. Thus to use the new kernel simply reboot.
6. Check the Installed Kernel
To check the installed kernel you can use the command:
uname -rIt will return the version of the installed kernel. Ideally you want to execute this command before and after the system reboot to check that the version of the kernel has changed.